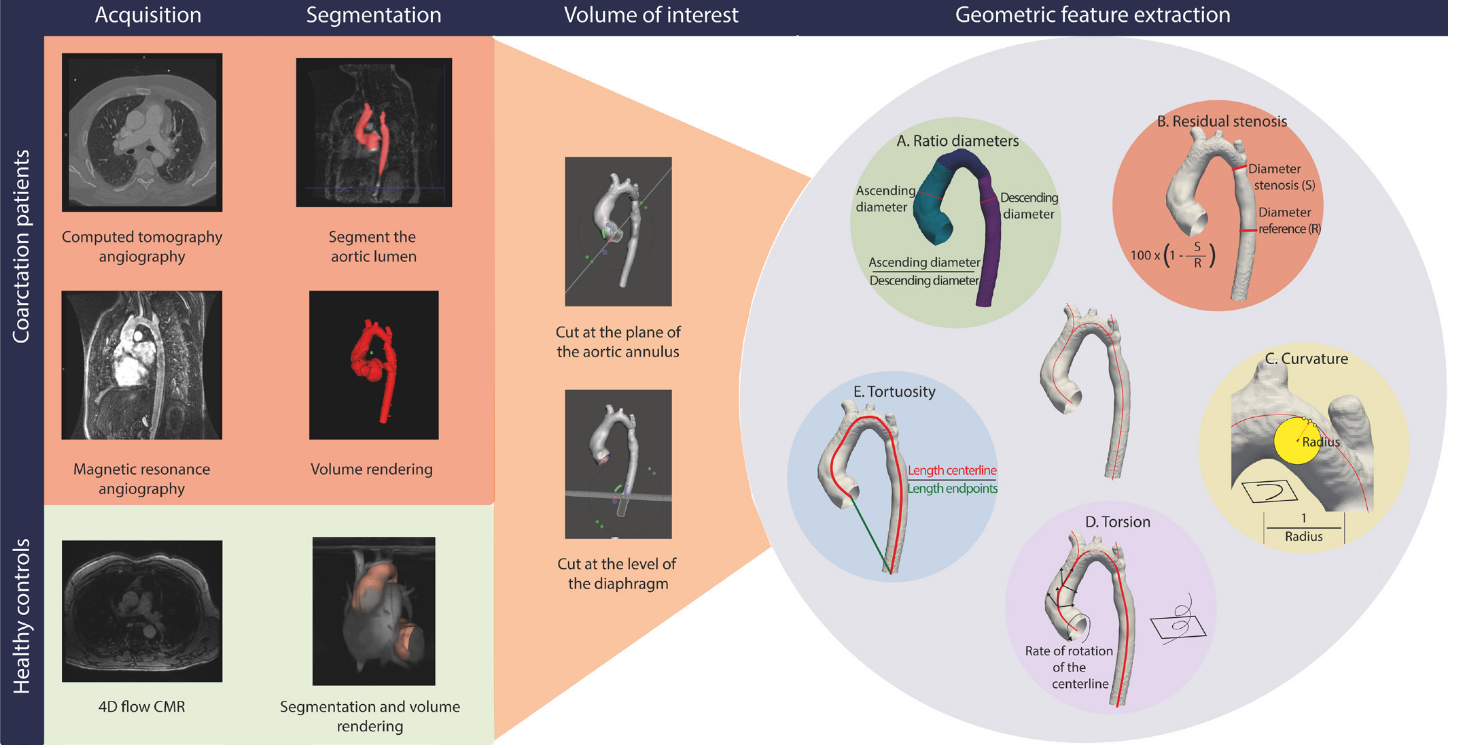
The centreline of each aortic volume was determined and based on this centreline, the curvature, torsion and tortuosity of the centreline were calculated using VMTK functions (figure 1). The centreline is a curve and the deviation of a curve from linearity and planarity is described by the curvature and torsion. Curvature is the degree of bending of the centreline, the deviation from a straight line in one plane and was defined as the inverse of the radius of the osculating circle (figure 1C). The torsion is the twist of the centreline in space, the degree of deviation of the curve from the osculating plane (figure 1D). Curvature and torsion were calculated with the standard VMTK functions (vmtkcenterlinegeometry). Tortuosity was defined as the ratio of the centreline length and the direct distance between the centreline endpoints
Minderhoud, S. C. S., van Montfoort, R., Meijs, T. A., Korteland, S.-A., Bruse, J. L., Kardys, I., Wentzel, J. J., Voskuil, M., Hirsch, A., Roos-Hesselink, J. W., & van den Bosch, A. E. (2024). Aortic geometry and long-term outcome in patients with a repaired coarctation. Open Heart, 11(1), e002642. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2024-002642